By Jason Keigher
•
March 20, 2025
As we age, our bodies change in ways that can make weight management more challenging. Metabolism slows down, muscle mass naturally decreases, and joint issues might limit mobility. Despite these challenges, maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for seniors to reduce the risk of chronic diseases, maintain independence, and enjoy a higher quality of life. Understanding Age-Related Weight Challenges Weight management for seniors requires a different approach than for younger adults. After 60, several factors influence your body's relationship with weight: Slower metabolism means fewer calories burned at rest Reduced muscle mass changes your body composition Hormonal changes affect how and where fat is stored Medications may influence weight as a side effect Joint pain or mobility issues might limit activity Effective Weight Loss Strategies for Seniors Focus on Nutrition Quality Rather than severe calorie restriction, seniors should prioritize nutrient-dense foods: Increase protein intake to preserve muscle mass (lean meats, fish, eggs, legumes) Choose high-fiber fruits, vegetables, and whole grains Stay hydrated with water rather than sugary drinks Limit processed foods, which often contain excess sodium and unhealthy fats Consider smaller, more frequent meals to maintain energy levels Appropriate Exercise Movement remains essential, but should be tailored to your abilities: Start with low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or chair exercises Include strength training 2-3 times weekly to preserve muscle mass Add flexibility and balance exercises to prevent falls Begin with short sessions and gradually increase duration Consider working with a trainer experienced in senior fitness Mindful Eating Practices Developing awareness around eating habits can make a significant difference: Eat without distractions to recognize fullness cues Slow down and enjoy each bite Use smaller plates to manage portions naturally Plan meals ahead to avoid convenience foods Recognize emotional eating triggers Safety Considerations Weight loss for seniors should always prioritize health and safety: Consult your healthcare provider before starting any weight loss program Aim for gradual weight loss of 1-2 pounds per week Never eliminate entire food groups without medical guidance Monitor how weight loss affects existing health conditions Adjust medications as needed with doctor supervision Success Beyond the Scale For seniors, the benefits of maintaining a healthy weight extend far beyond appearance: Improved mobility and independence Better management of chronic conditions like diabetes and heart disease Reduced joint pain and improved arthritis symptoms Enhanced energy levels and mood Lower risk of falls and injuries Remember that healthy aging isn't about reaching an ideal weight but about maintaining functionality, independence, and quality of life. Small, sustainable changes to diet and activity levels can make a significant difference in how you feel and function in your golden years.

By Jason Keigher
•
December 28, 2024
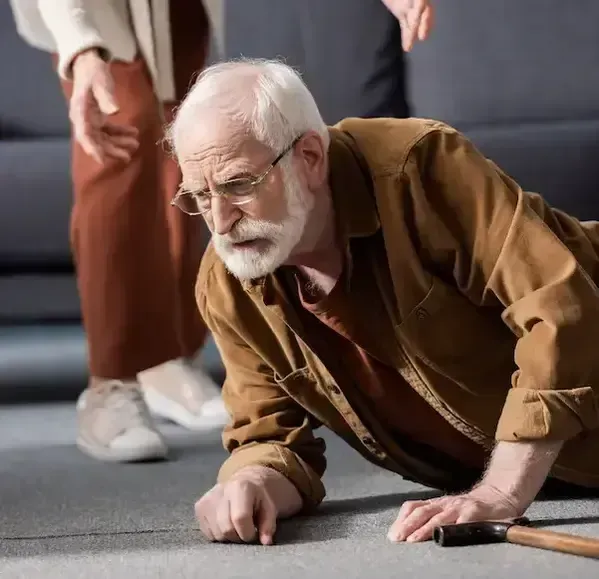
As we age, it’s common to experience decreased balance and mobility. Unfortunately, this can increase the risk of falling, and knowing what to do afterward is crucial for your safety and confidence. Being able to safely get up from the floor after a fall is a skill that can prevent additional injuries and provide peace of mind. However, there’s even greater value in reducing the chances of falling in the first place. This blog will outline both key areas and how my personalized training services can help you or a loved one.
By Jason Keigher
•
October 30, 2024
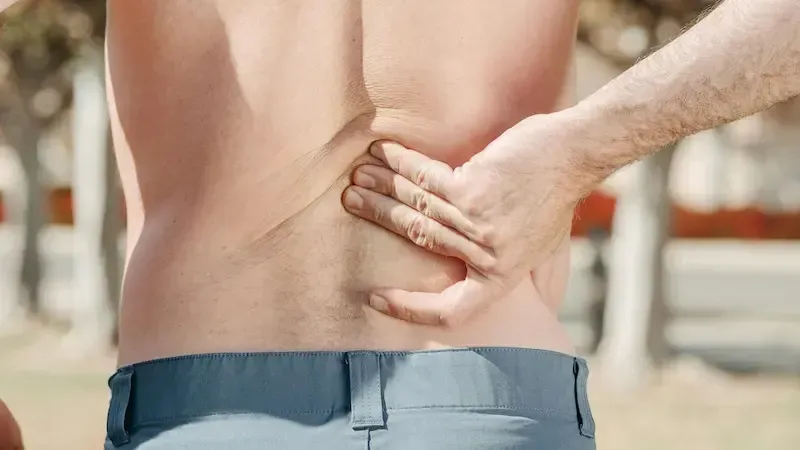
Back pain is a common issue among seniors, often resulting from age-related changes in the spine, arthritis, or muscle weakness. While back pain can make exercise seem daunting, regular physical activity is one of the most effective ways to manage pain, improve mobility, and enhance overall health. At Senior Fitness Palm Springs, we design customized workout programs to help seniors safely and effectively alleviate back pain and regain strength.
By Jason Keigher
•
October 30, 2024
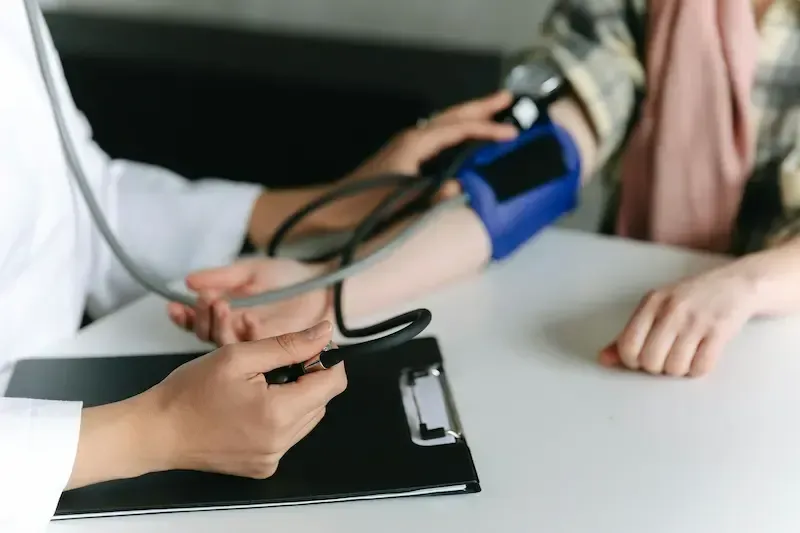
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a common condition among seniors that can lead to serious health problems like heart disease and stroke. However, regular exercise is one of the most effective ways to manage blood pressure naturally. With the guidance of a personal trainer, you can create a customized fitness plan that addresses your specific needs, helping you stay active and healthy. At Senior Fitness Palm Springs, we specialize in designing safe and effective exercise programs to help seniors manage high blood pressure and improve their overall health.

By Jason Keigher
•
October 30, 2024
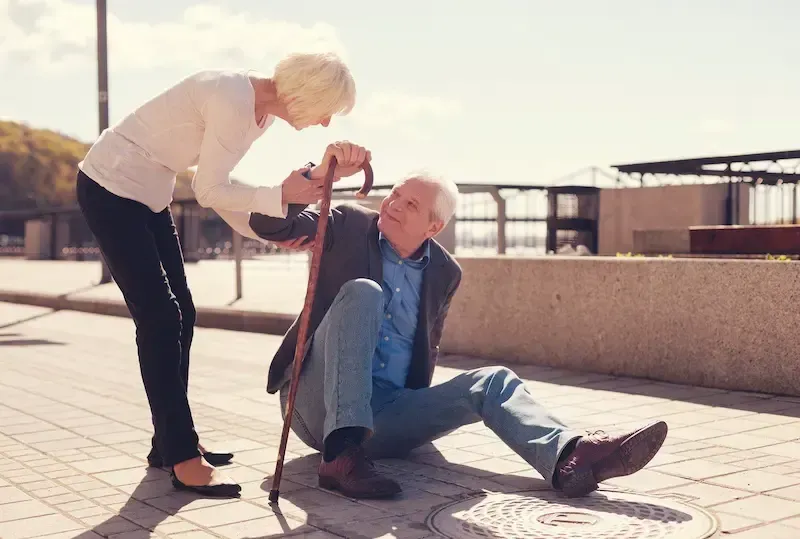
Falls are a leading cause of injury among seniors, but regular exercise can help improve balance, strengthen muscles, and enhance coordination, all of which contribute to reducing the risk of falls. At Senior Fitness Palm Springs, we focus on safe and effective exercises designed to improve balance and stability, helping seniors maintain independence and confidence in their daily activities.
By Jason Keigher
•
October 30, 2024
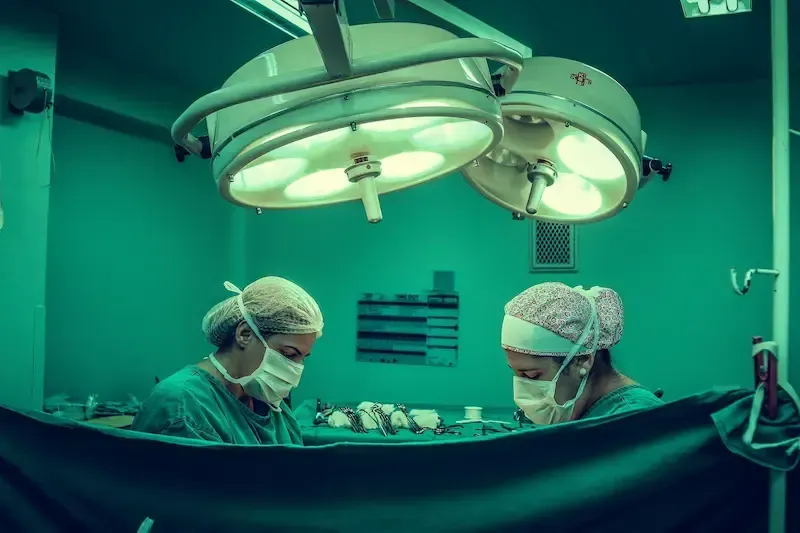
Recovering from surgery can be challenging, especially for seniors. Regaining strength and flexibility is essential for a successful recovery and a return to daily activities. At Senior Fitness Palm Springs, we specialize in personalized post-surgery fitness plans that focus on safe, gradual rebuilding of strength and flexibility, helping seniors recover faster and regain their independence.

By Jason Keigher
•
October 30, 2024
Living with chronic pain can make daily activities challenging, but staying active is one of the most effective ways to manage pain and improve overall health. Regular exercise can help reduce pain, increase mobility, and enhance quality of life for seniors. At Senior Fitness Palm Springs, we specialize in creating personalized exercise programs that focus on safely managing chronic pain while improving strength, flexibility, and endurance.

By Jason Keigher
•
October 30, 2024
Cognitive decline, including conditions like mild cognitive impairment and dementia, can significantly impact a senior's ability to perform daily activities and maintain independence. However, regular exercise has been shown to improve cognitive function, slow the progression of cognitive decline, and enhance overall quality of life. At Senior Fitness Palm Springs, our certified trainers provide personalized exercise programs designed to support seniors with cognitive challenges, helping them stay active, engaged, and mentally sharp.

By Jason Keigher
•
October 21, 2024
Parkinson's disease is a progressive neurological disorder that affects movement, balance, and coordination. While there is no cure, regular exercise can help manage the symptoms, improve overall quality of life, and slow the progression of the disease. At Senior Fitness Palm Springs, we understand the unique challenges faced by seniors with Parkinson's and offer personalized exercise programs designed to enhance mobility, strength, and independence.

By Jason Keigher
•
October 13, 2024
Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition characterized by widespread pain, fatigue, and tenderness in the muscles and joints. For seniors living with fibromyalgia, staying active may seem challenging, but regular exercise is one of the best ways to manage symptoms, improve flexibility, and enhance overall quality of life. At Senior Fitness Palm Springs, we specialize in designing low-impact exercise programs tailored to the needs of seniors with fibromyalgia, helping them stay active safely and comfortably.

By Jason Keigher
•
October 7, 2024
Anxiety and depression can affect people of all ages, but seniors often face unique challenges that contribute to these conditions, such as health issues, loss of loved ones, or reduced social interaction. Regular exercise has proven to be a powerful tool in managing anxiety and depression by enhancing mood, reducing stress, and promoting overall mental health. At Senior Fitness Palm Springs, we design personalized exercise programs that help seniors stay active, engaged, and mentally well.
SENIOR Fitness Tips and Advice: The SENIOR Fitness PALM SPRINGS Blog
Stay updated with the latest Senior fitness tips, health advice, workout routines, and more on the Senior Fitness Palm Springs Personal Training blog.
GET IN TOUCH
Senior Fitness Palm Springs
1717 E Vista Chino
A7-209
Palm Springs, CA 92262

